
Why do MES and IT projects often go over budget?
Making the decision to implement a manufacturing execution system is just the tip of the iceberg. The next stage is to refine the details of
A good production system ensures optimal utilisation of resources, both human and material, enhances the efficiency of production processes, ensures quality control, and facilitates real-time monitoring and management of the entire production process. It should be flexible, adaptable, and capable of evolving with the technological landscape, ensuring that the business remains competitive and agile.
Efficiency: Optimises the production process, reducing waste and maximising output.
Flexibility: Adapts to changes in production volume and variety effortlessly.
Quality Control: Ensures that products meet the set manufacturing industry quality standards consistently.
Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time data for informed decision-making and manufacturing processes.
Scalability: Grows with your manufacturing business, accommodating increased demand seamlessly.
Virtually all industries that manufacture physical products can benefit from using the manufacturing software solutions.
Manufacturing software can help businesses in these industries to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase profitability. Here are just a few of the ways that manufacturing software can benefit the manufacturing businesses in:
Improved production planning and scheduling: Manufacturing software can help businesses to optimize their production process by planning and scheduling production runs efficiently. This can help to reduce waste and improve on-time delivery performance.
Better inventory management: Manufacturing software can help businesses to track inventory levels in real time and optimize their inventory replenishment process. This can help to reduce inventory costs and ensure that businesses always have the materials they need on hand.
Enhanced quality control: Manufacturing software can help businesses to improve quality control by tracking product defects and identifying areas where the production process can be improved. This can help to reduce the number of defective products that are produced and improve customer satisfaction.
Increased collaboration: Manufacturing software can help businesses to improve collaboration between different departments, such as production, engineering, and sales. This can help to streamline processes and improve communication throughout the organisation.
Production software is instrumental in managing and optimising the manufacturing process. Various types of production software cater to different needs, ensuring that businesses of all sizes and types can find solutions that fit their specific requirements. Here are some common types:

Poor production planning and scheduling: Manufacturing software can help you optimize your production process by planning and scheduling production runs efficiently. This can help to reduce waste and improve on-time delivery performance.
Inefficient inventory management: Manufacturing software can help you track inventory levels in real time and optimize your inventory replenishment process. This can help to reduce inventory costs and ensure that you always have the materials you need on hand.
Poor quality control: Manufacturing software can help you improve quality control by tracking product defects and identifying areas where the production process can be improved. This can help to reduce the number of defective products that are produced and improve customer satisfaction.
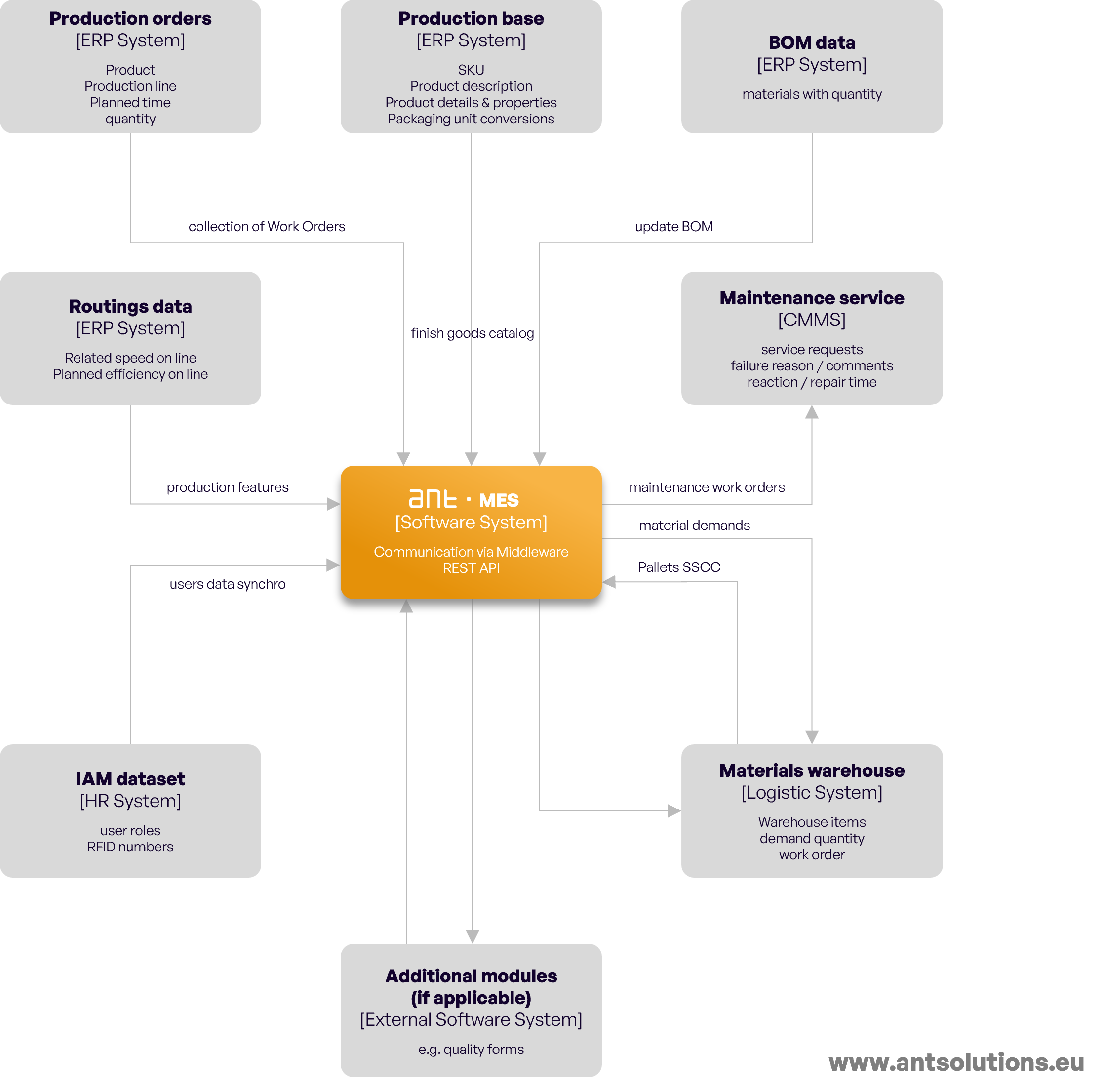
The integration of production systems offers various methods to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between different components. These integration options include web services, which enable real-time interactions over the internet, RFC (Remote Function Call) for connecting SAP systems, intermediate databases for storing and sharing data, and versatile flat files like XML and CSV formats, which simplify structured data transfer. These diverse integration pathways empower organisations to efficiently synchronise their production systems, ensuring a harmonious flow of information across the entire operational landscape.
Improved data visibility and flow: Integration can help to break down the silos that often exist between different manufacturing software systems, providing a single source of truth for data. This can improve data visibility and flow across the organization, leading to better decision-making.
Increased efficiency and productivity: Integration can automate manual tasks and streamline processes, freeing up employees to focus on more value-added activities. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity across the manufacturing operation.
Reduced costs: Integration can help to reduce costs by eliminating duplicate systems and data entry, and by improving operational efficiency.
Improved customer satisfaction: Integration can help to improve customer satisfaction by enabling businesses to deliver products and services on time and to budget.
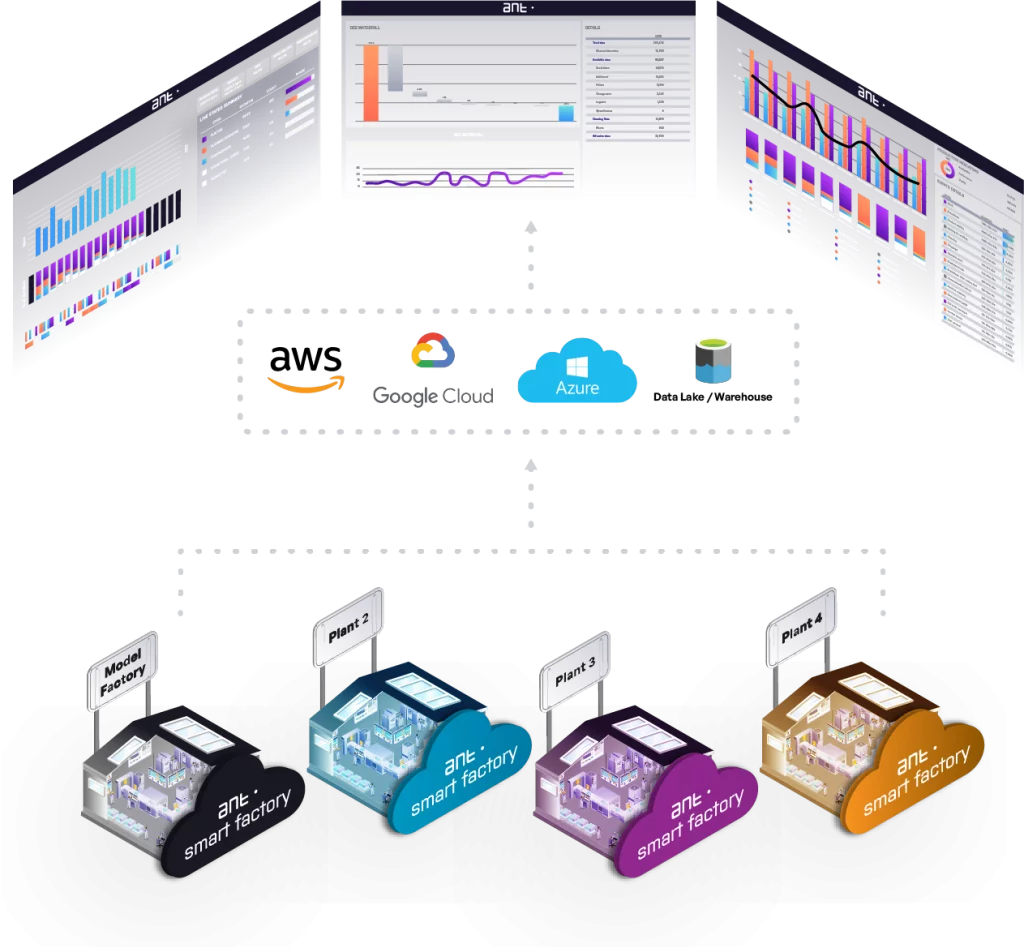
Cloud Manufacturing
Cloud manufacturing is the innovative application of cloud computing within the manufacturing sector. ANT Solutions offers a cloud-based manufacturing systems that leverage the power of the cloud to enhance manufacturing efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Our systems provide manufacturing companies with a comprehensive solutions for managing, diagnosing, monitoring, and controlling production lines, ensuring optimal performance and integration across all departments involved in production.
Horizontal Integration: Cloud-based production software improves horizontal integration across the supply chain, providing end-to-end visibility into the manufacturing process.
Emissions Tracking: Factories can monitor their carbon emissions in real-time, helping them set and track progress towards reduction goals.
Dynamic Production Scheduling: The system allows for dynamic adjustments to production schedules based on real-time demand and other factors.

Analytic tools beyond simple OEE and SPC calculations that leverage machine learning to realize use cases like project management and predictive maintenance

Devices sitting next to generating equipment that act as operator interfaces, data pre-processing engines, etc.

Software developer kits and other tools that enable 3rd parties to build modules / extensions on top of the solution which can optionally be promoted on marketplaces.
Step by step digital instructions and documentation for operators at assembly stations and lines to follow paperless production. Include images, movies, documents. Monitor action time for optimisation.




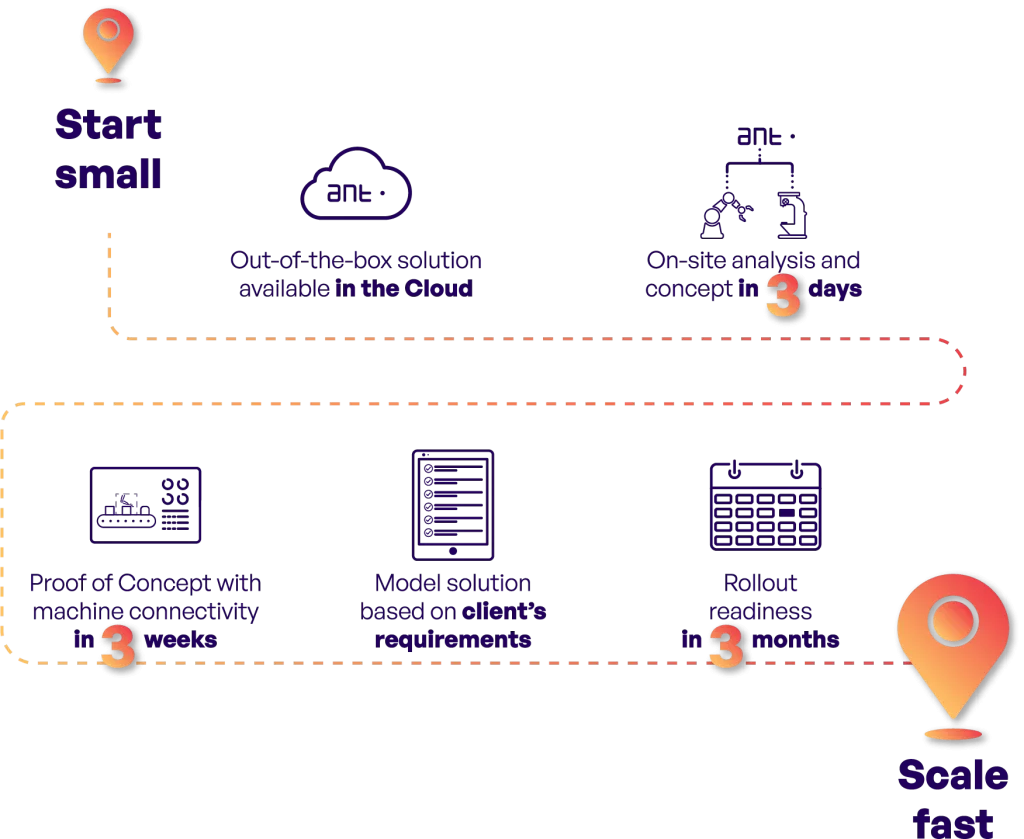
Starting your digital transformation involves a well-defined roadmap that will progressively guide manufacturing processes in your factory toward increased efficiency and digital maturity. Here’s how to set the wheels in motion for your production digitisation:
Establish a Foundation: Kick-off by creating a solid wired network infrastructure. A dependable network is essential for connecting machinery and collecting data, which forms the cornerstone of your digital transformation.
Integrate and Optimize: Next, implement production software to analyse data and elevate your Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). Build out your MES to streamline operations, integrating it with ERP systems to foster a synchronized data ecosystem across your facility.
Expand and Refine: Finally, enhance your digital landscape with advanced planning, scheduling systems, and comprehensive maintenance management software. Integrate a WMS for superior inventory control and adopt paperless systems. Utilize an EMS to align production costs with energy consumption for more sustainable operations.


Making the decision to implement a manufacturing execution system is just the tip of the iceberg. The next stage is to refine the details of

What is production optimisation? Production optimisation is the process of identifying and implementing improvements to production processes in order to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and

Machine data acquisition software is a tool that enables the collection, storage, processing and visualisation of data from machines and equipment. This data can be
By providing your email and clicking the “Sign up” button, you agree to subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest news and useful insights about manufacturing.
By providing your email and clicking the “Download a catalogue” button, you agree to receive our newsletter.