MIcro stops
monitoring
The most effective system for FMCG for monitoring production rates and downtime
What are micro stops and why are so important?
Micro stops are unplanned machine stoppages that, depending on the individual plant approach, last up to 1 minute, 2 minutes, – 5 minutes, above this time such a stoppage qualifies as an unplanned stoppage. These are short-lived incidents, but if you count them over a shift, a week, or a month, you realize that they account for a large proportion of our production. These stoppages are playing a key role in hight volume industry such as FMCG where speed of production is a crucial factor accounting for a final result.
Is this improvement necessary to me?
- You know your OEE but you haven`t good root causes analysis
- You have identified production lines with the unknown and high number of stoppages
- You work in a factory with implemented OEE but with no specialised software to analyse upcoming data
Why ANT Micro Stops Monitoring System?
Unlock the power of real machine data to drive lean actions and prevent downtime. Reduce the time spent on manual reporting of machine states by operators, and delve into deep analyses to understand why your machines lose availability.
Enable seamless machine communication by utilizing standard TCP and native PLC protocols like OPC DA/UA and Siemens. Retrieve vital data from the automation layer, including production counters, machine statuses, and essential process parameters.
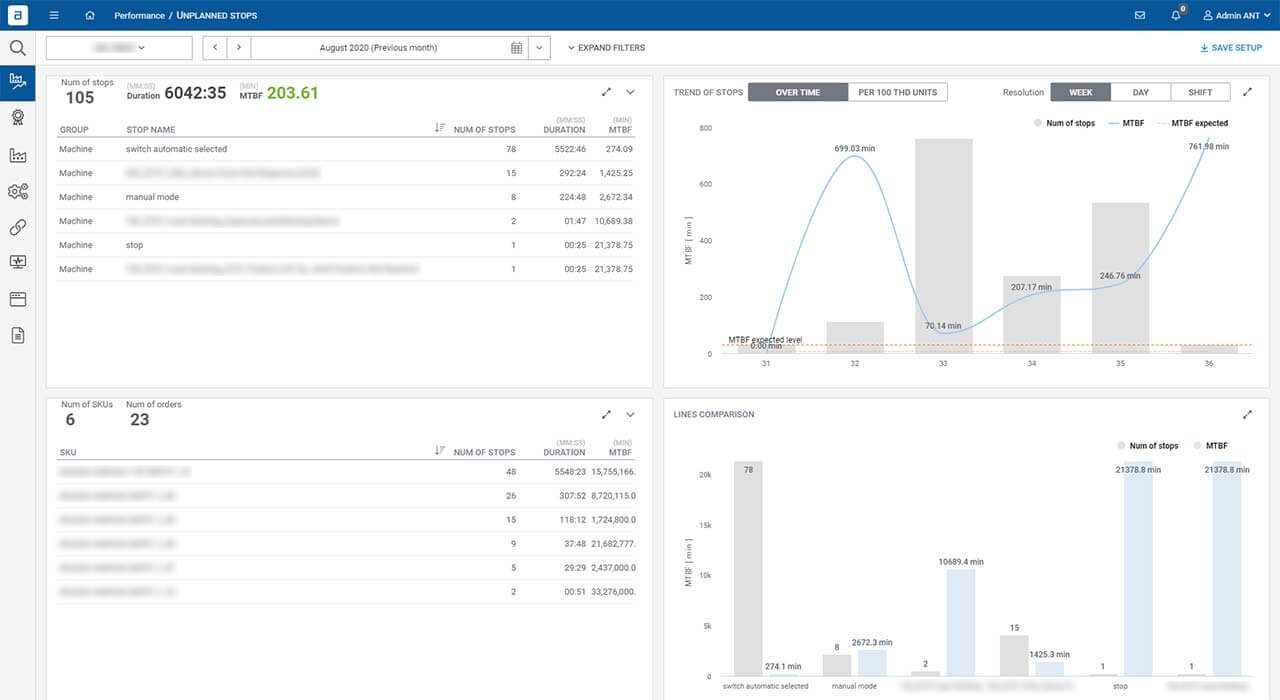
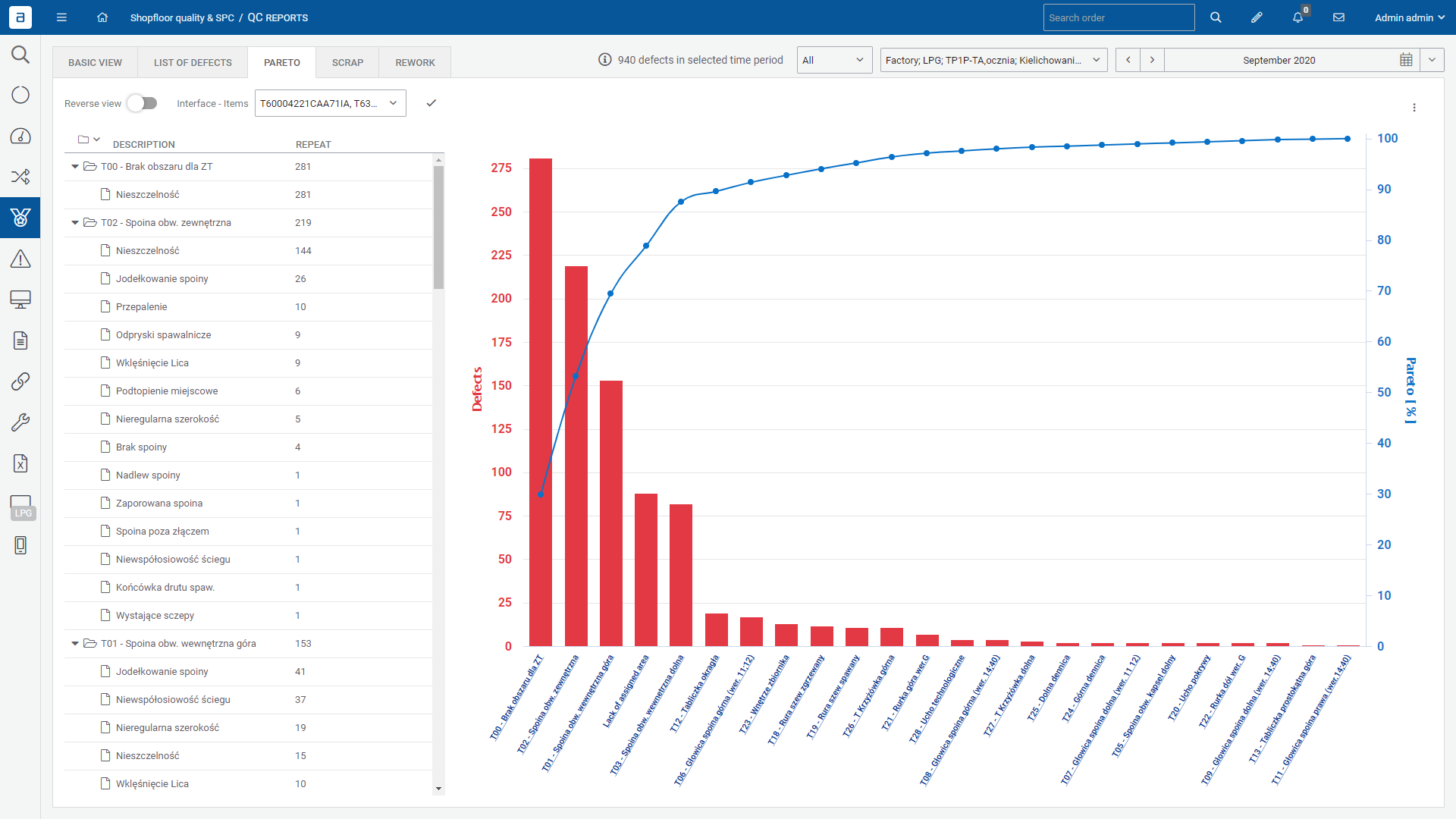
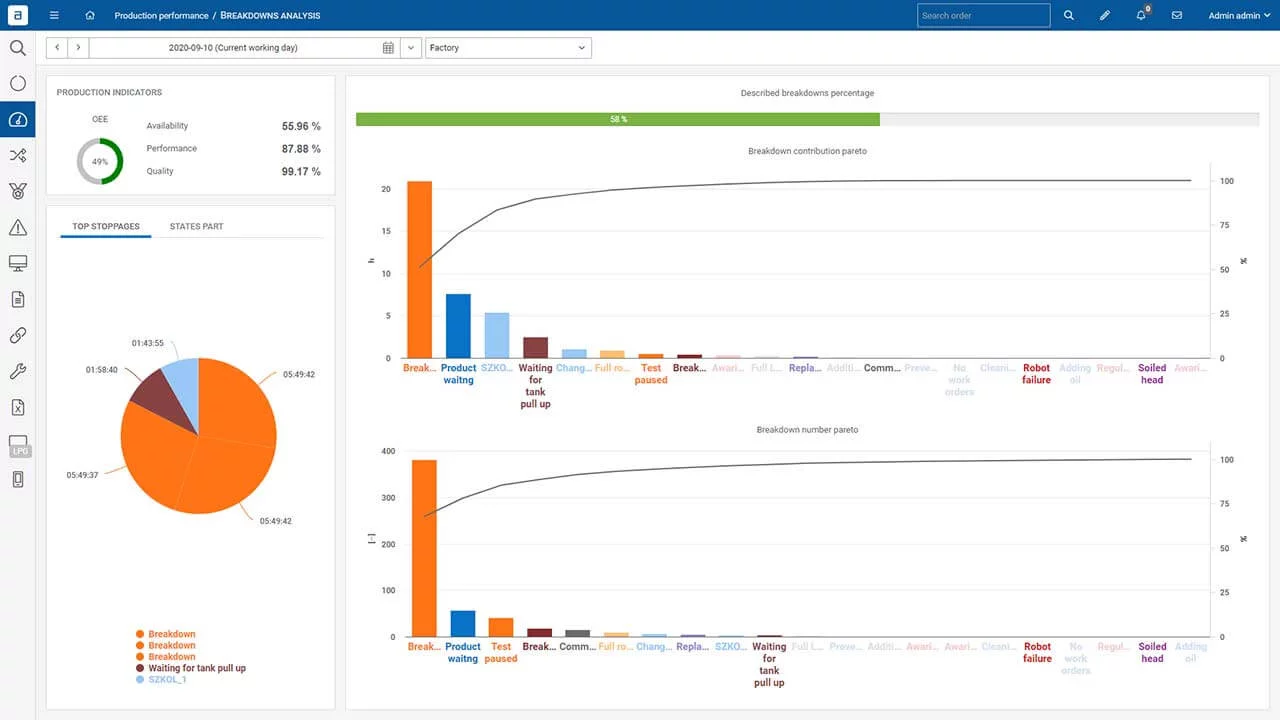
Experience the advantage of a transparent overview encompassing all areas, coupled with in-depth top-to-bottom analysis. Our dedicated dashboards empower you with rapid problem and trend recognition, ensuring efficient decision-making.
How does it work?
ANT’s AI detects responsible machine in the line.
- Registering each, even the shortest stop of the machine with its reason from PLC
- Reading alarms from PLC
- Algorithm assigns responsible machine if in the line
- Real machine data for lean actions to stop the stops
- Less time to manually report machine states by Operator
- Deep analyses why machine looses its availability
What is our approach?
In order to mitigate the number of micro stops, the ANT team goes through 3 steps.
Identification
Phase
We analyse current factory state and create a plan
Identifying and naming micro stops
- to define micro stops by machine.
- to define the time between micro stops and failures
- to create a list of all possible micro stops that can occur on a machine.
Connectivity
Phase
Our group of engineers connects machines on-site
How to collect data?
The quickest way is to connect directly to a PLC driver – such a connection allows the ANT team to access data such as machine states, state times, failure codes, production, waste counters, and more. If the machine is older or not equipped with a PLC driver, our team can add an I/O communication module to fetch the information about machine states and times.
Without the possibility to identify alarm codes the operator will have a greater share of the process, as he or she will have to describe the condition from a list of the most common micro steps by hand, choosing pre-made code from the dictionary. The bottom line is that all this data is real, as it is collected directly from the machines.
The collected data from the PLC will bring a lot of alarm codes, which have to be grouped and assigned to specific microswitches which allow for doing more precise analysis.
Analysis
Phase
We help to analyse collected data and get the insights
Analysis of the collected data:
Analysing the operation of the line for a selected period of time – the range is arbitrary (shift/day/week/year), the manager can select the state of interest and, using the “drill down” method, get information about:
- What was the cause of the micro stop?
- How many micro stops there were during a given order (number of occurrences)?
- What was their total time?
- What was the share of this condition in the entire production?
In summary, with the right tools line manager can identify the dark area that causes micro stops. By connecting directly to the machines, the system has real data about the times and causes of downtime. The operator can easily describe undescribed downtimes, and management has a lot of properly grouped data with which it can reduce or completely eliminate micro stops. This is how we deal with the problem of micro downtime at our clients.
How fast can get Return of Investments on ANT Micro Stops Moniotring Solution?
AVG OEE GROWTH
Based on real factory results
AVG MTBF GROWTH
Based on real factory results
Testimonials
Machine Efficiency Loss Analysis, with focus on complexity impacts and machine reliability
Reliable reporting, Insights into aggregated results, tactical use for shiftly/weekly prioritization per Loss Category. 100% flexibility in accounting for user’s KPI standards, good understanding of Lean Manufacturing KPIs
Tonci M., Global Manufacturing Systems Manager
BAT Croatia

Thanks to MES system we are able to tracking a present production situation information about failures and potential risks – all information might to be recalculated into KPI Table supporting a Management proces.
MES system are integrated with existing data system which are feeding it into data from devices PLC, status of orders etc.
Rafał P., Digital Project Leader
Food & Beverages Company

System Presentation
Contact with our Expert

Why to get a demo?
- A 60-minute online meeting with a dedicated specialist presenting a top system from an industry similar to yours
- Live modeling of your production process
- A budget quotation after the meeting
Related articles

How to increase production transparency on the factory shopfloor?
Transparency in manufacturing may sound like a marketing ploy, but it actually brings tangible benefits, from smoother workflows to significant financial savings. If transparency in

What are the causes of micro-stoppages during the manufacturing process?
Learn about the common causes of micro-stoppages during the manufacturing process and how to address them to improve efficiency and productivity.

ANT Microstops (production monitoring, performance) system on SMD (FMC), FMD, THP, and OTP in Tobacco factory
The factory was in a phase of digital transformation, which included digitalization, working methodology, and IWS ready methodology. Tobacco production is characterized as a high-speed
Microstops are small interruptions that happen in a production line which result in downtime for machines or other production equipment. They can be caused by either machine malfunction or human error, making it hard to identify where exactly these microstops are happening.
The machine connectivity data is then used to identify where these microstops are happening and take corrective measures so that they don’t happen again in future production cycles.
Microstops can be detrimental to the production process and should be monitored closely. They are often overlooked by supervisors because they don’t have an immediate impact on production output and can go unnoticed for hours, leading to significant OEE drops and missing deadlines.
Indentyfiing microstops helps to increase OEE and boost overall production efficiency.



