The implementation of a MES system is a complex and costly process that requires careful planning and preparation. A key step is to conduct a pre-implementation audit, which will help to identify the needs and capabilities of the organisation and assess whether a MES system is the right solution.
A MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is software that supports the management of production processes in real time. The MES system collects data from machines, devices, and other IT systems, and then uses it to monitor, analyse, and optimise production processes.
A pre-implementation audit of a MES system is a process that aims to investigate the needs and capabilities of the organisation and assess whether a MES system is the right solution. The audit covers the analysis of the following areas:
Business goals: The audit should define what business goals the organisation wants to achieve through the implementation of a MES system.
Production processes: The audit should analyse the current production processes and identify areas where a MES system can bring the greatest benefits.
Production infrastructure: The pre-implementation assessment should determine the technical condition of machines and equipment and check whether the production infrastructure is sufficient to support the MES system.
IT infrastructure: The audit aims to outline the technical condition of the IT infrastructure and check whether the MES system is compatible with existing IT systems.
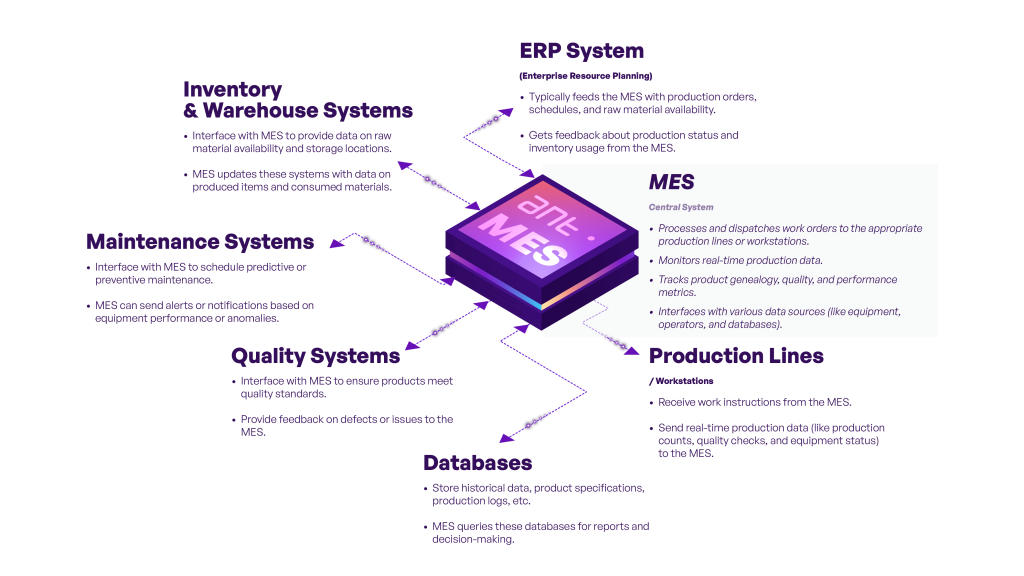
Integrations with other systems: The audit evaluates which systems should be integrated with the MES system.
Vendors: Finally, pre-implementation activities should analyse the competencies and experience of MES system vendors.
A pre-implementation audit of a MES system is an essential step that helps to increase the chances of success of the system implementation. The assessment helps to identify potential obstacles and challenges to implementation, adapt the MES system to the specific needs and requirements of the organisation, and also plan a successful and efficient implementation of the MES system.
Project scope
The initial stage of the pre-implementation audit is to establish the scope of the MES implementation project, which should include the following elements:
Business goals: The audit should define what business goals the organisation wants to achieve through the implementation of a MES system. Business goals should be clearly defined and measurable. Examples of business goals that can be achieved through the implementation of a MES system include:
- Increased production efficiency
- Reduced production costs
- Improved product quality
- Reduced lead time
- Increased production flexibility
Production processes: The assessment should analyse the current production processes and identify areas where a MES system can bring the greatest benefits. Examples of areas where a MES system can bring benefits include:
- Production planning
- Production execution
- Quality control
- Inventory management
- Document management
MES modules: The audit should also define which MES modules are essential to achieve business goals. Examples of MES modules include:
- Production
- Quality
- Warehousing
- Documentation
- Human resources
- Finance
Defining the scope of the MES implementation project is a key step that allows for accurate planning and preparation of the implementation process.
Audit of machines and infrastructure
An audit of machines and production infrastructure is essential to determine whether machines and equipment are sufficient to support the MES system.
During the audit, the following elements should be checked:
Technical condition of machines and equipment: It should be checked whether machines and equipment are in good working order and do not require repairs or modernisation.
Performance of machines and equipment: It should be checked whether machines and equipment are sufficiently efficient to meet production requirements.
Compatibility of machines and equipment with the MES system: It should be checked whether machines and equipment are compatible with the MES system in terms of interfaces and communication protocols.
Production infrastructure: It should be checked whether production infrastructure, such as electrical network, telecommunications network, and emergency power systems, is sufficient to support the MES system.
If the machines and production infrastructure are not sufficient to support the MES system, appropriate actions should be taken to adapt them.
Examples of actions that can be taken to improve the compatibility of machines and production infrastructure with the MES system:
Modernisation of machines and equipment: In the case of outdated or insufficiently efficient machines and equipment, their modernisation or replacement can be considered.
Adapting machines and equipment to the MES system: In some cases, it may be necessary to adapt machines and equipment to the MES system by adding appropriate interfaces and communication protocols.
Development of production infrastructure: In the case of insufficient infrastructure, its development can be considered, such as by expanding the electrical or telecommunications network.

IT audit
An audit of IT infrastructure is essential to determine whether IT infrastructure is sufficient to support the MES
During the audit, the following elements should be checked:
Technical condition of IT infrastructure: It should be checked whether IT infrastructure, such as servers, network devices, and software, is in good working order and does not require repairs or modernisation.
Performance of IT infrastructure: It should be checked whether IT infrastructure is sufficiently efficient to support the MES system.
Compatibility of the MES system with existing IT systems: It should be checked whether the MES system is compatible with existing IT systems in terms of interfaces and communication protocols.
If the IT infrastructure is not sufficient to support the MES system, appropriate actions should be taken to adapt it.
Examples of actions that can be taken to improve the compatibility of IT infrastructure with the MES system:
Modernisation of IT infrastructure: In the case of outdated or insufficiently efficient IT infrastructure, its modernisation or replacement can be considered.
Adapting the MES system to existing IT infrastructure: In some cases, it may be necessary to adapt the MES system to existing IT infrastructure by adding appropriate interfaces and communication protocols.
Integrations
The MES system should be integrated with other IT systems, such as ERP, WMS, CMMS, and APS. For this purpose, it is necessary to:
- Define which systems should be integrated
- Choose the appropriate integration method
- Test the integration process
Vendor selection
Selecting an MES system vendor is a key step in the implementation process. A well-chosen vendor will provide an MES system that meets the organisation’s requirements and provide support and service after implementation.
When choosing a vendor, the following elements should be checked:
Vendor’s competencies and experience: It should be checked whether the vendor has the appropriate competencies and experience in supplying MES systems.
Vendor’s references: The vendor’s references from other customers should be checked.
Post-implementation support and service: The type of post-implementation support and service offered by the vendor should be checked.
Examples of actions that can be taken to choose the right MES system vendor:
Develop a list of potential vendors: Research should be conducted to identify potential vendors.
Send out requests for proposals: Requests for proposals should be sent to potential vendors.
Evaluate proposals: Vendor proposals should be evaluated in terms of competence, experience, references, and post-implementation support.
To summarise
A pre-implementation audit of an MES system is an essential step that helps to increase the chances of success of the system implementation. The audit helps to identify the needs and capabilities of the organisation, understand potential challenges and threats, and also plan a successful and efficient implementation of the MES system.
Products related to this article

MES System – Manufacturing Execution System – ANT Solutions
System MES – Manufacturing Execution System 0 % operating time increase 0 % defects quantity reduction 0 % material consumption reduction 0 % changeovers time

CMMS System for Maintenance Management
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) Plan, manage and react with CMMS System by ANT. The best maintenance system for equipment performance in your factory. It

OEE Performance monitoring
Performance Monitoring (OEE) Connect and gather data from your machines. Schedule a Demo They Trusted Us: Key Benefits OEEincrease ✔️ shorter downtimes ✔️ faster production

